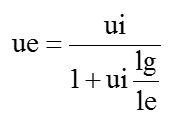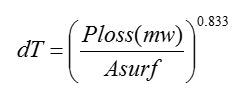Standard Transformer Applications
General Transformer Glossary
- Input Voltage/Current
- Output Voltage/Current
- Frequency
- Topology/Duty Cycle
- OCL/Leakage Inductance.
- Temperature rise
- Ambient Temperature. Ta70B
Safety Related Info
-
Output Voltage Limit
- EN60950… SELV for 42.4Vpk or 60VDC
- UL5085… Class II 30Vmax & Class III 30-100V or 150V
- EN61558-2-6… 50VRMS/120V ripple free DC
-
Transformer Class
- Class I/II/III in EN60950/EN61558 -> Protection
- Class I/II/III in UL5085 -> Voltage
Safety related info
-
Insulation Grade
- Class A 105C -> 100C max
- Class E 120C -> 115C max
- Class B 130C -> 120C max
- Class F 155C -> 140C max
- Class H 180C -> 165C max
-
TEX-E or Twisted Wire
-
MW82 wire and etc.
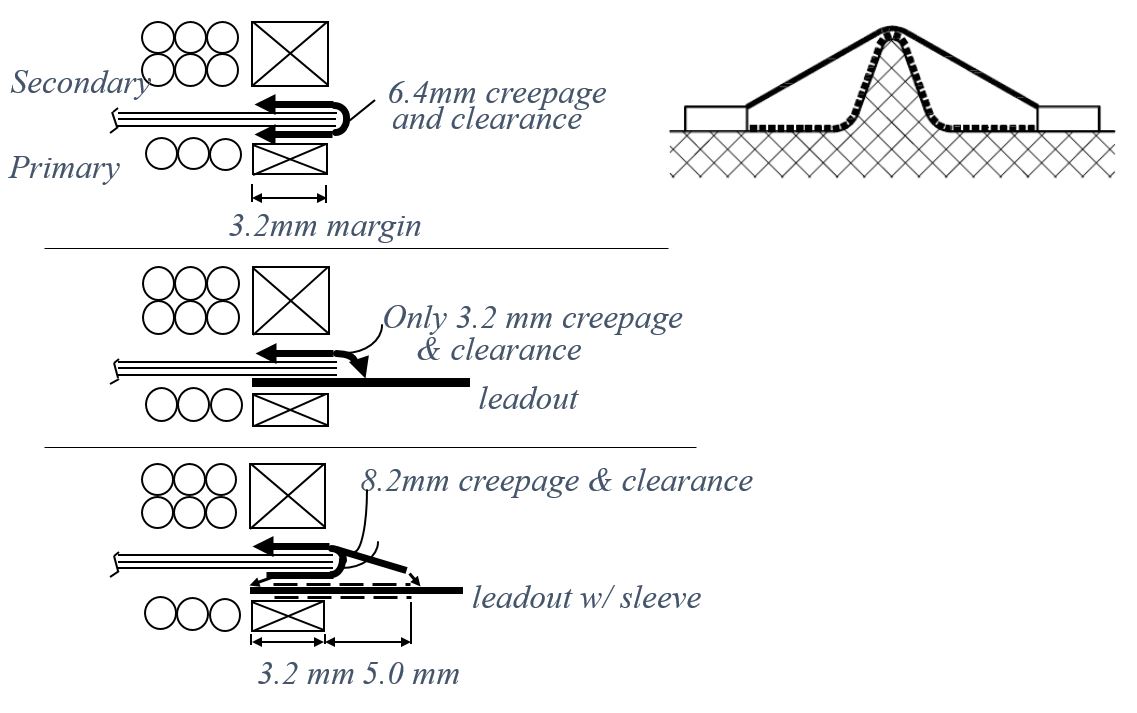
Creepage and Clearance
Laminated Transformer Types
- Print PCB Transformer
- UI Core low profile pin type transformer
- Current Sensing Transformer
- Lead type transformer
- Power everywhere
- New edge why still use the laminated transformer?
Laminated transformer materials
- Lamination material
Lamination: Z11, H12, H14, H18, H23, H50
- Standard Sizes
EI28/30/35/41/48/57/66
- Insulation materials
Bobbin (PET, NYLON), TAPE (Polyester), Varnish (C1105, AC43)
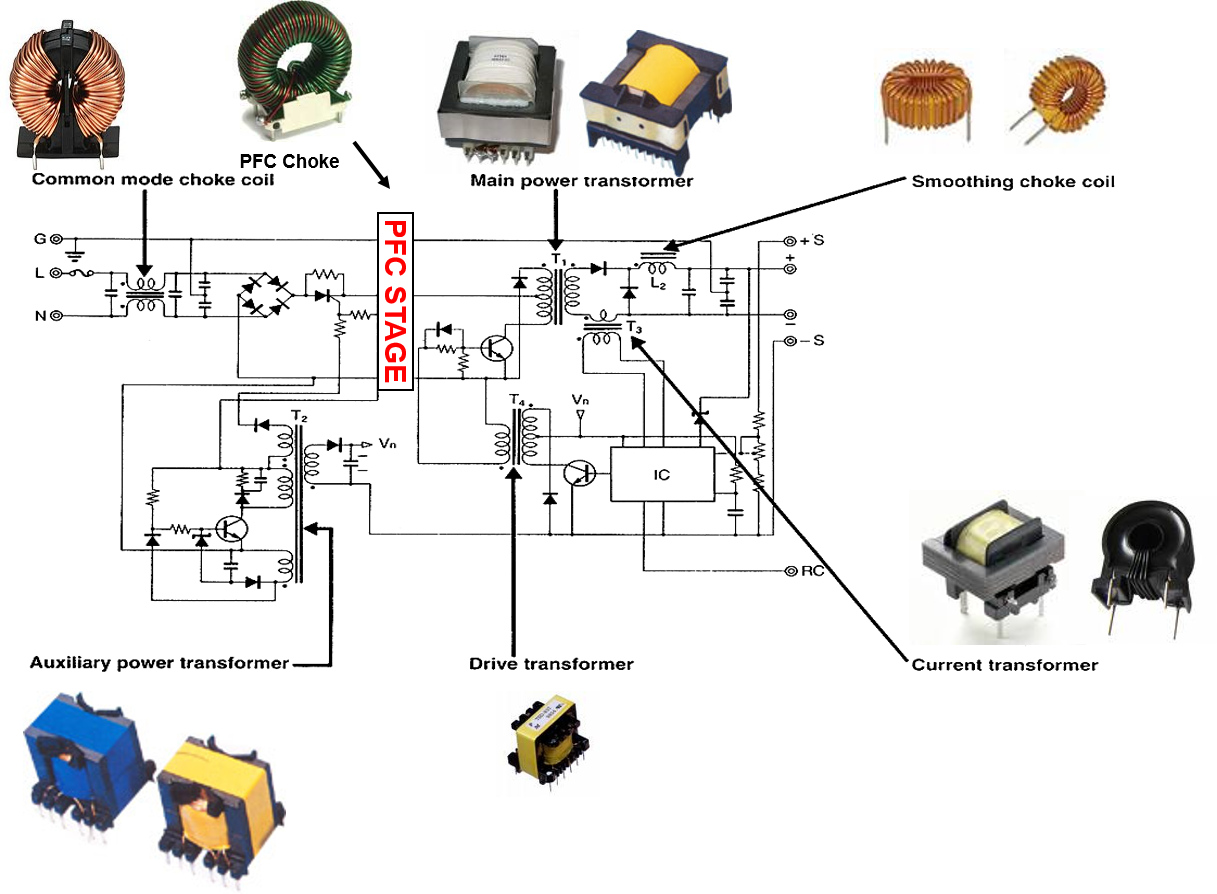
Standard Ferrite Magnetics SMPS Application
Choke Types
-
Choke Types by Application
- Common Mode Choke
- Differential Mode Choke
- Energy Stock Choke (PFC, BUCK)
-
Choke Types by Material
- Ferrite Core
- Powdered Core (iron, MPP, Sendust)
- Laminated Core (EI, taped, Amorphous)
Ferrite XFMR Types
-
Ferrite XFMR Types by Application
- Flyback XFMR (with Gap)
- Forward XFMR
- PushPull
- Full bridge
-
Ferrite XFMR Types by Shapes
- EE 13, EE 16… …
- EFD20,
- ER28, ETD34…
- Planar E40
Ferrites (continued)
-
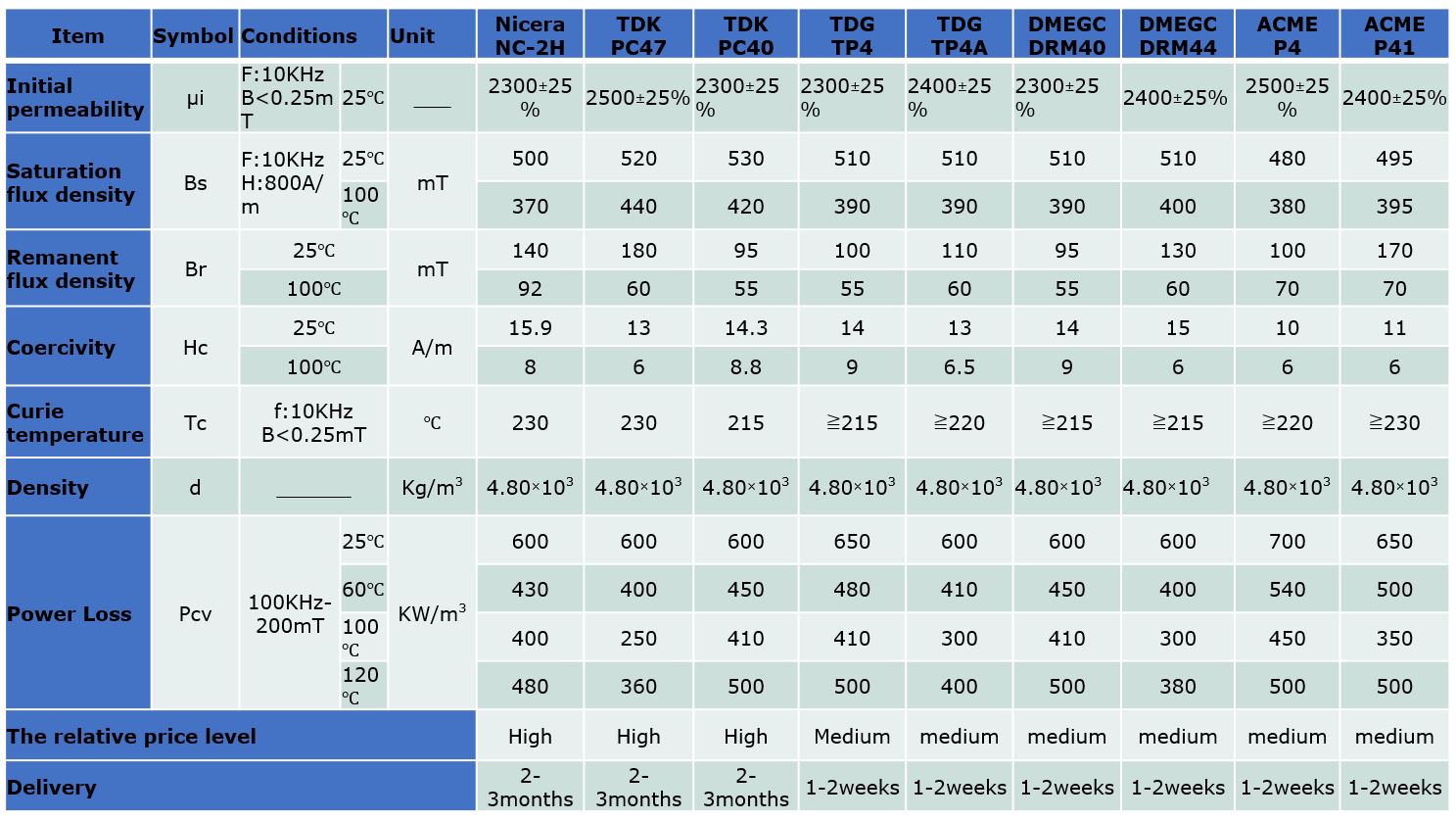
Ferrite XFMR Material
- TDK PC-40
- Nicera NC-2H
- China Material TDG, DMEGC ……
-
Ferrite XFMR Bobbins
- EE 13, EE 16… …
- EFD20,
- ER28, ETD34…
- Phenolic PM9820 T375J
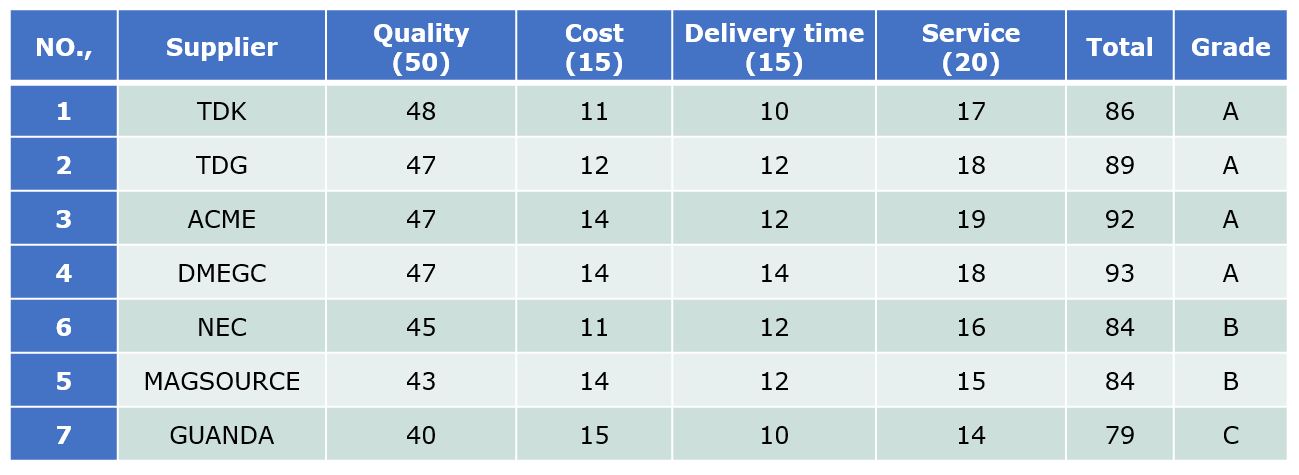
Core Suppliers
Key Parameters Affect to your power supply
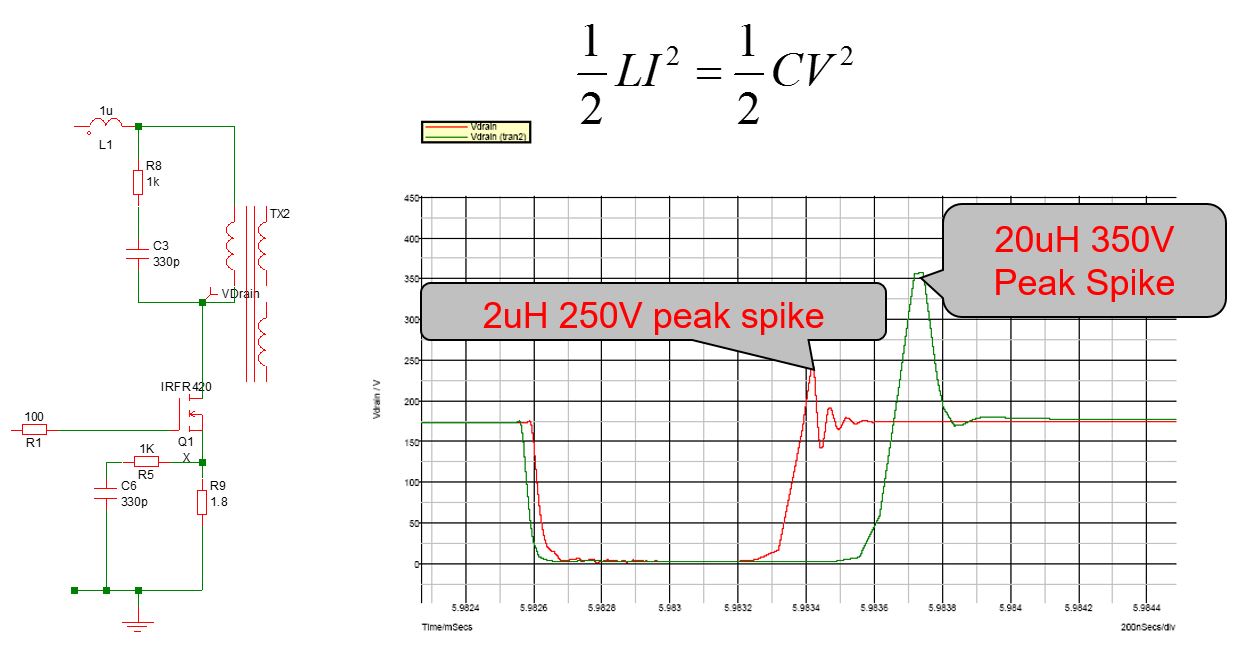
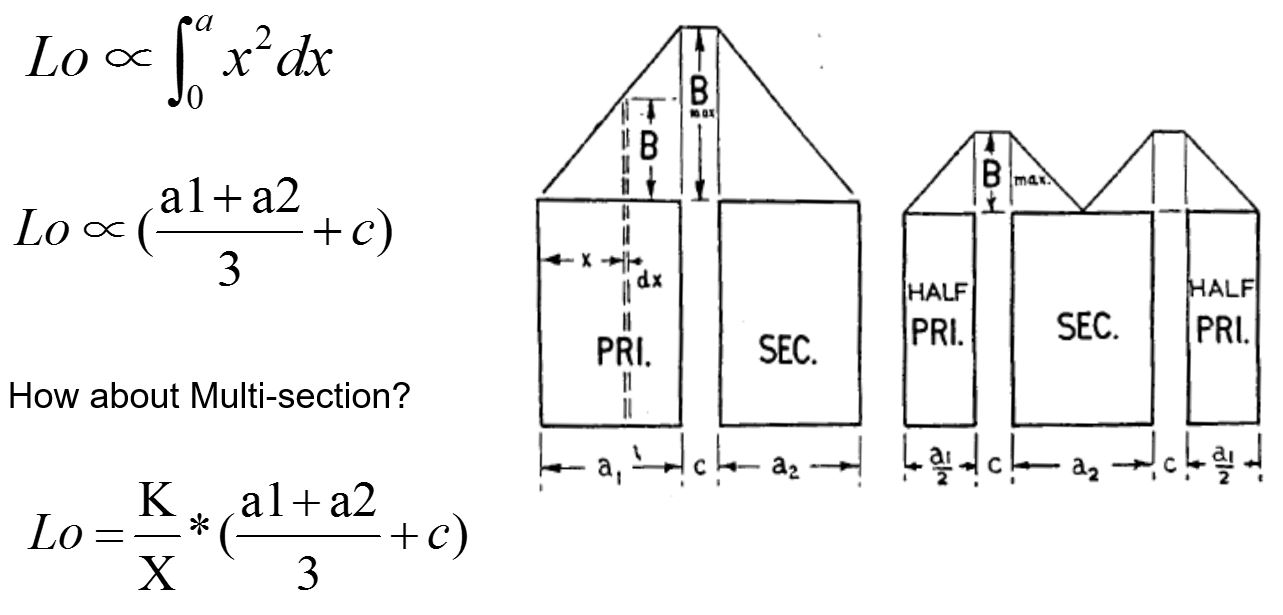
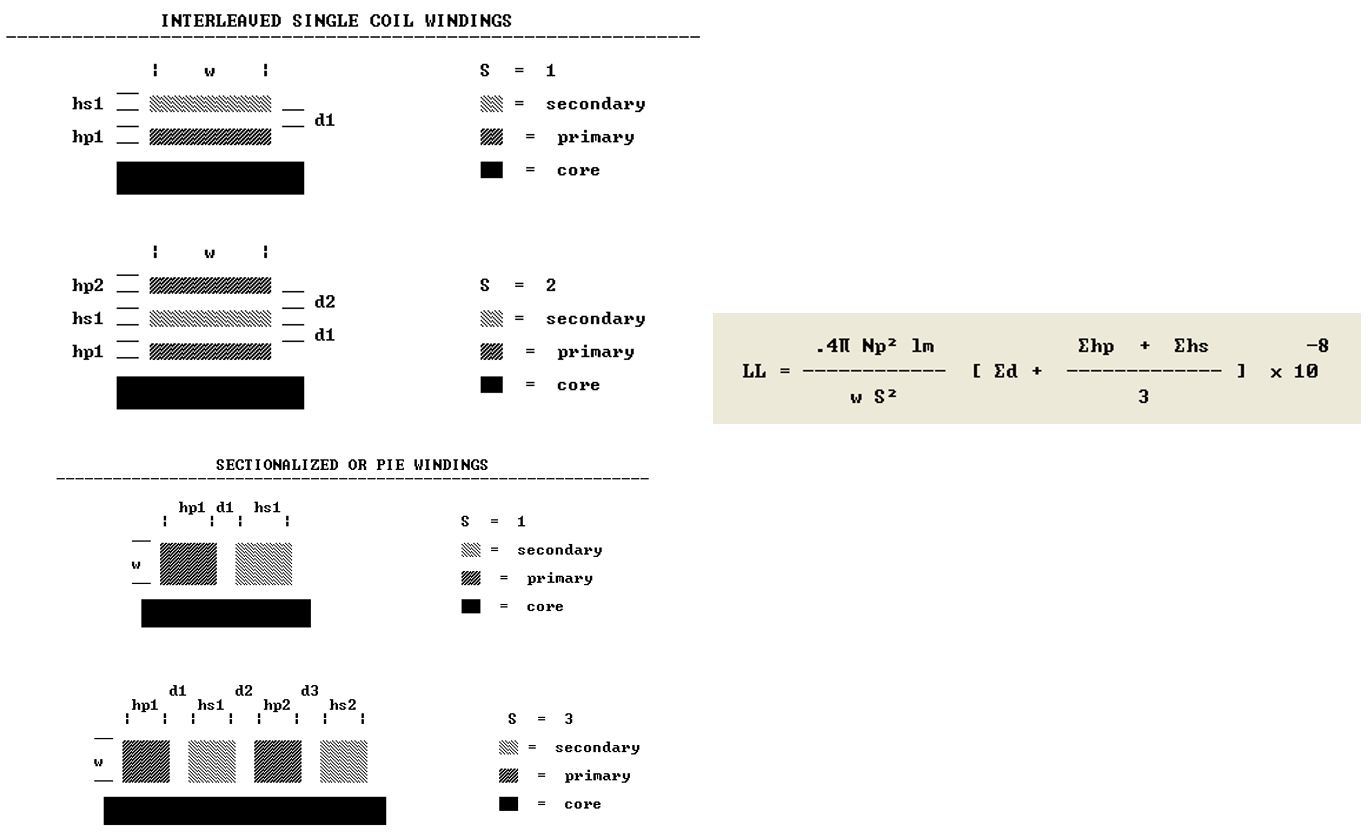
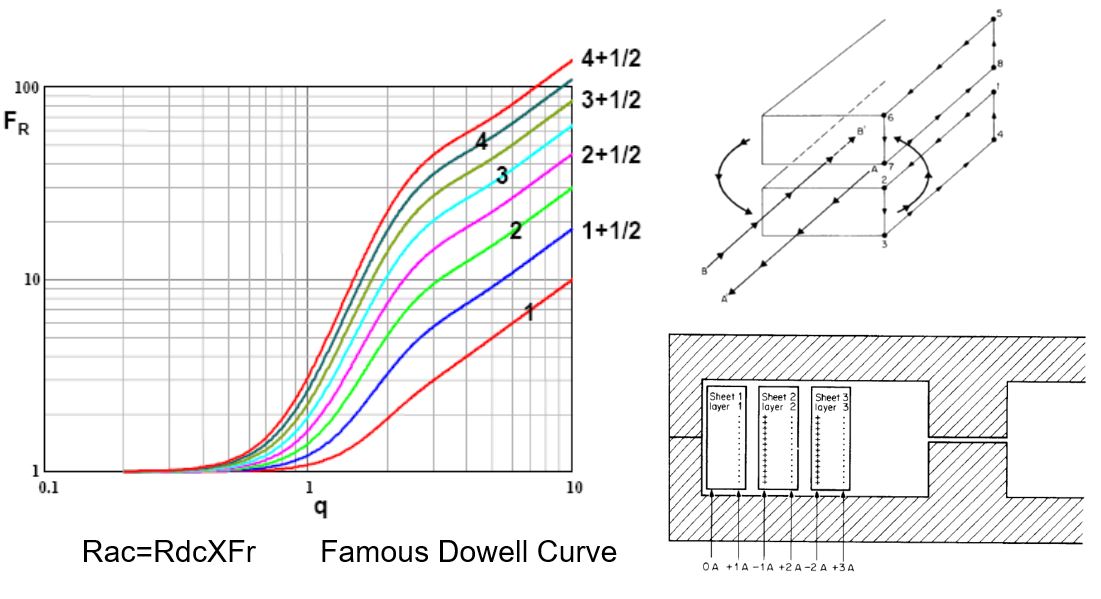
Leakage Inductance
Key Parameters Affect to your power supply
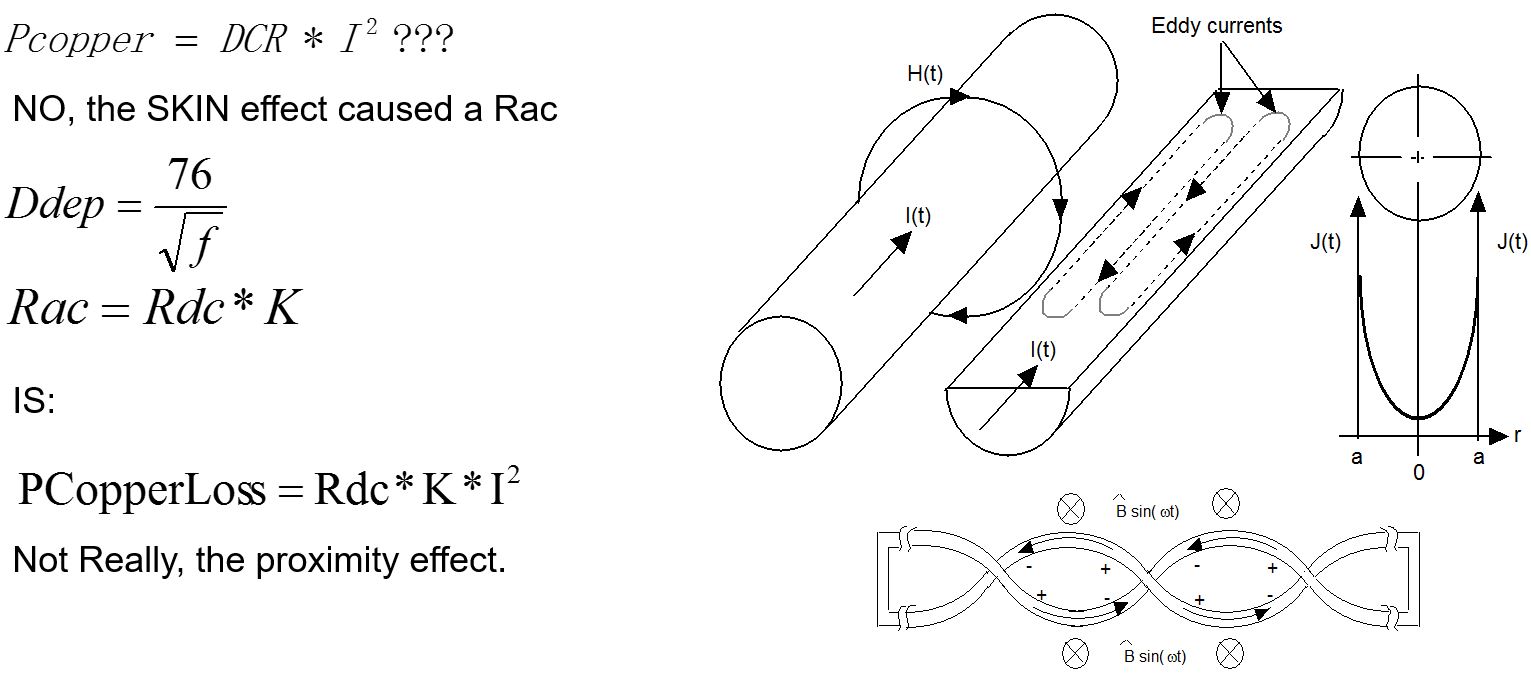
Wire Diameter Skin Effect Copper loss
- Minimize eddy currents using Leitz wire bundle. Each conductor in bundle has a diameter less than a skin depth.
- Twisting of paralleled wires causes effects of intercepted flux to be canceled out between adjacent twists of the conductors. Hence little if any eddy currents.
Proximity Effect
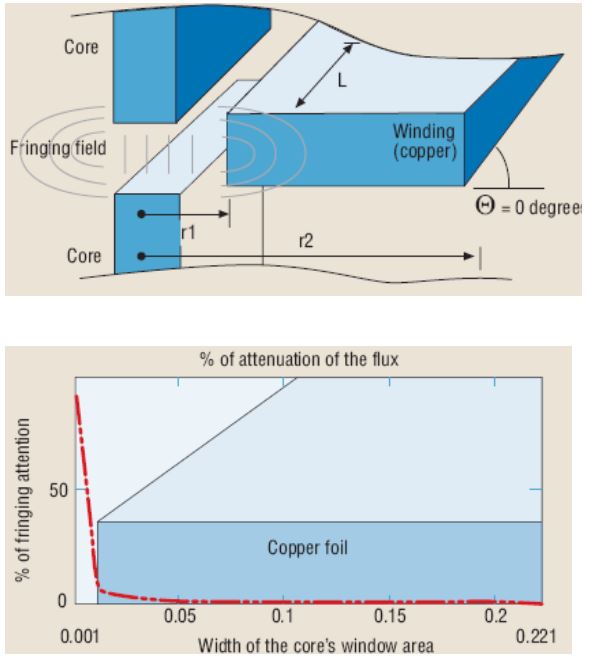
Gap Fringing Effect
- Fringing cause significant eddy loss
- Avoid the fringing loss by design
- Fringing increases the OCL
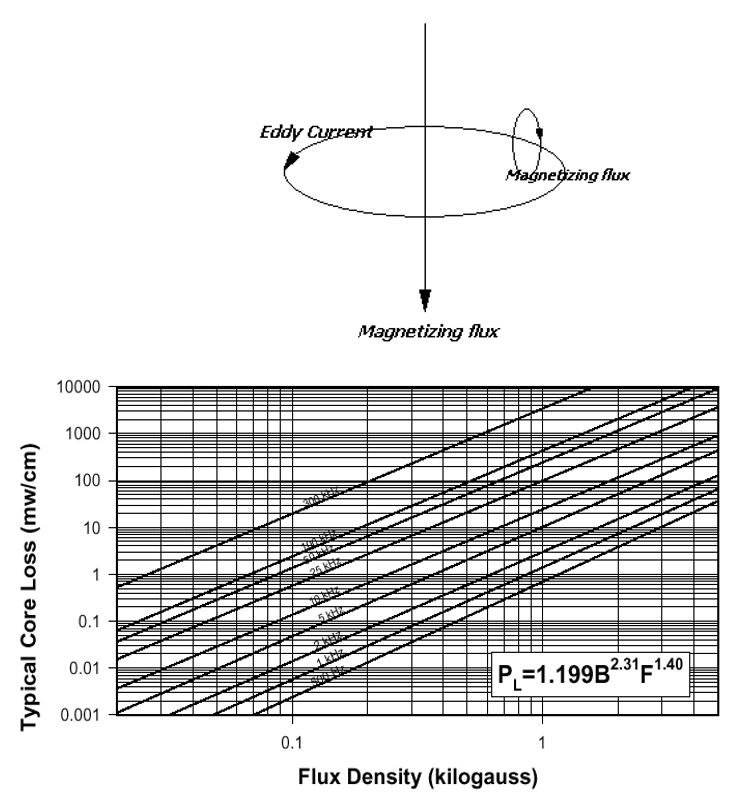
Core Losses
- Core Loss mW/cm^3 or mW/gram
- Different loss from different material
- Select right materials
Not over design
- B vs Core loss
No stress design
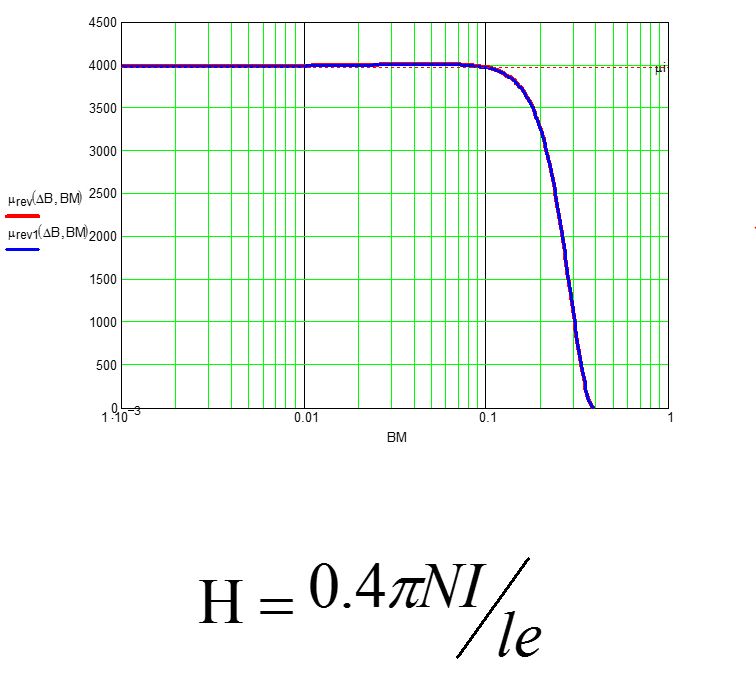
Gap, ue, Bdc
- Bsat -> inherent characteristics
- Bdc -> decided by peak current
- OCL -> decided by turns and gapping size
- Basic formula:
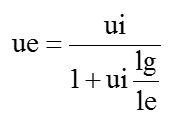
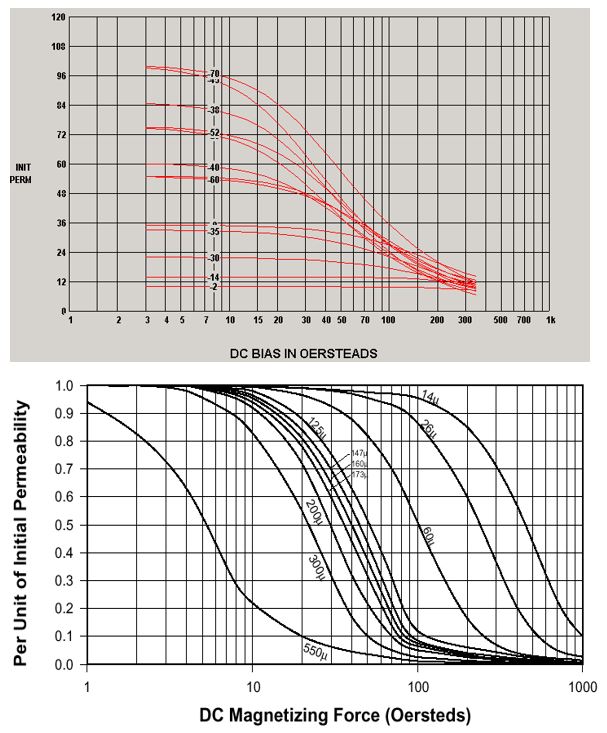
Powder Core Characteristics
- Distribute gap
- Soft Saturation
- Different power size -> different core loss
- Thermal Aging issue
- Choose right core materials
Common Mode Choke
- Impedance
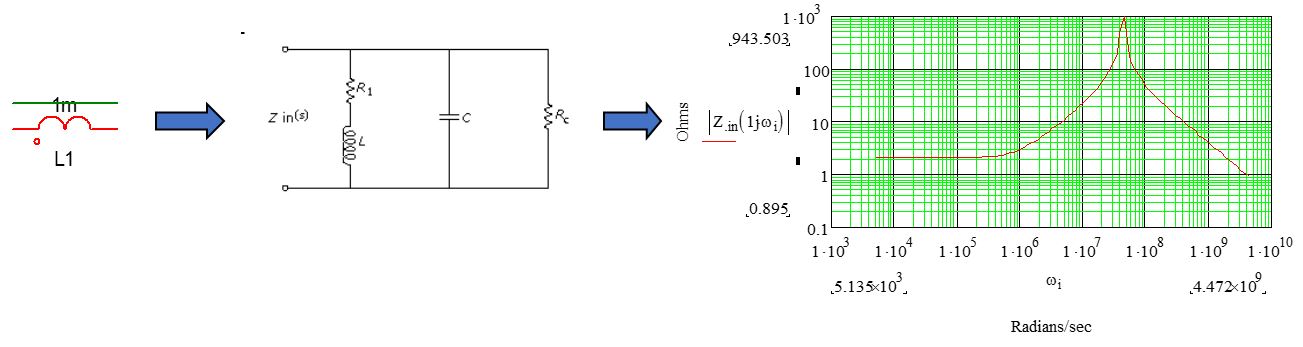
- EMI Filtering Network
- Mostly are low pass LC filtering circuit.
EMI Filtering Net Work
Magnetics Thermal Engineering
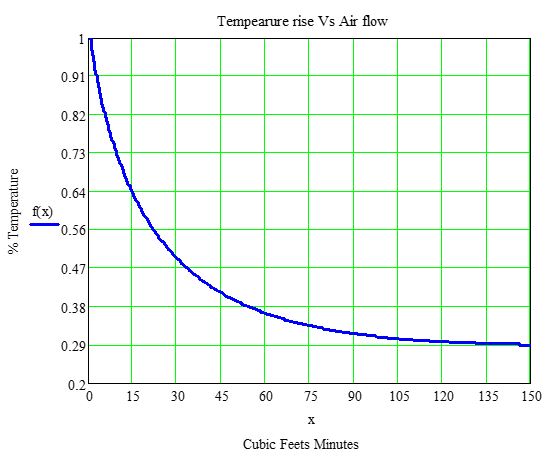
- Temperature Rise. Ploss includes copper loss and core loss
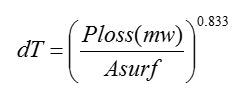
- Forced Ventilation Effect
Reference
- Leakage Inductance by N.H. Crowhurst 1949
- Soft Ferrites, Properties and Applications, 2nd Edition 1988 by Snelling E.C.
- Switching Mode Power supply Handbook by Keith. H. Billings
- Micrometals Catalogue Edition 2000
- ZETTLER Magnetics Catalog
- www.zettlermagnetics.eu